
Endoplasmic reticulum Biology lessons, Plant cell, Animal cell
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a large, dynamic structure that serves many roles in the cell including calcium storage, protein synthesis and lipid metabolism. The diverse functions of the ER are performed by distinct domains; consisting of tubules, sheets and the nuclear envelope. Several proteins that contribute to the overall architecture.
5.9 The Endoplasmic Reticulum Biology LibreTexts
Endoplasmic Reticulum Diagram. Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) is the tubular membrane inside the cytoplasm of the cell. Also, ribosomes cover their surface. Besides, the ER has both smooth and rough surface. In addition, they help in the transportation process. Transportation of food material, water and minerals in the body of a living organism.

Endoplasmic Reticulum Nursing school studying, Complex systems, The cell
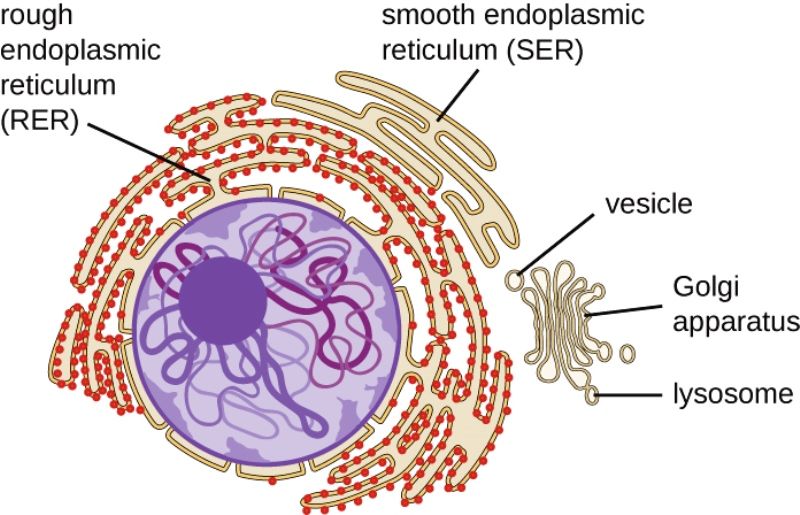
The endomembrane system ( endo - = "within") is a group of membranes and organelles in eukaryotic cells that works together to modify, package, and transport lipids and proteins. It includes a variety of organelles, such as the nuclear envelope and lysosomes, which you may already know, and the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus.

Rough And Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum In Plant Cell Rough And Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
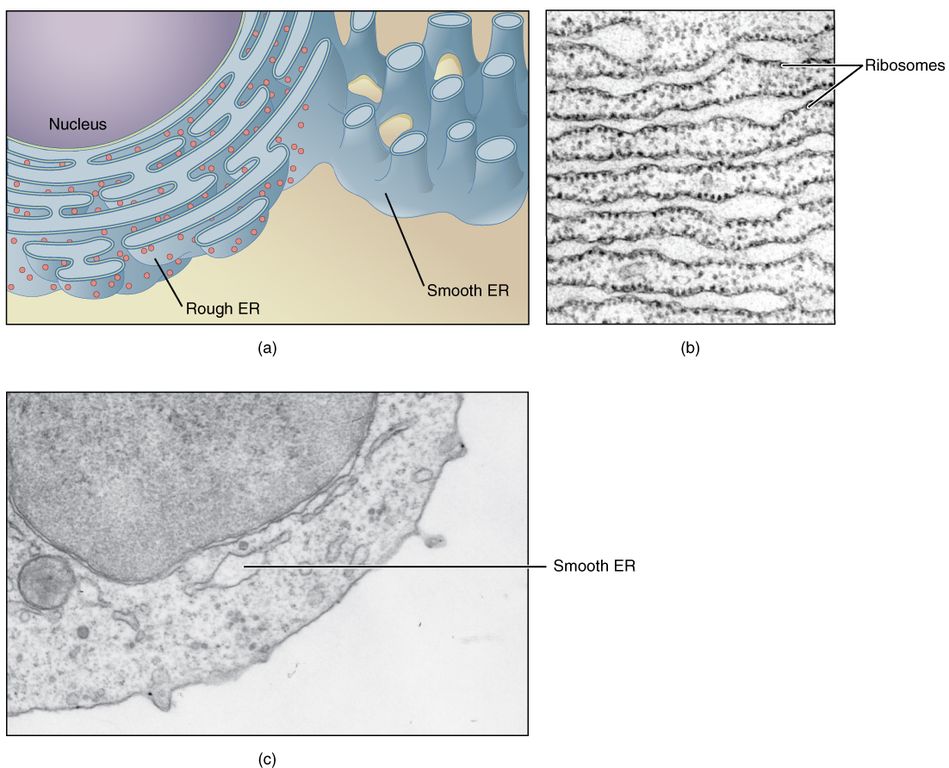
The ER can be classified in two functionally distinct forms: smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER) and rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER). The morphological distinction between the two is the presence of protein-synthesizing particles, called ribosomes, attached to the outer surface of the RER.The functions of the SER, a meshwork of fine tubular membrane vesicles, vary considerably from cell to.

Endoplasmic Reticulum Definition, Function, Structure Biology Dictionary
ADVERTISEMENTS: In this article we will discuss about the structure of endoplasmic reticulum. This will also help you to draw the structure and diagram of endoplasmic reticulum. 1. It was discovered by Porter (1945) as fine recticulum in endoplasm of cells and named as endoplasmic reticulum (E.R.). 2. It is a complex interconnecting system of […]
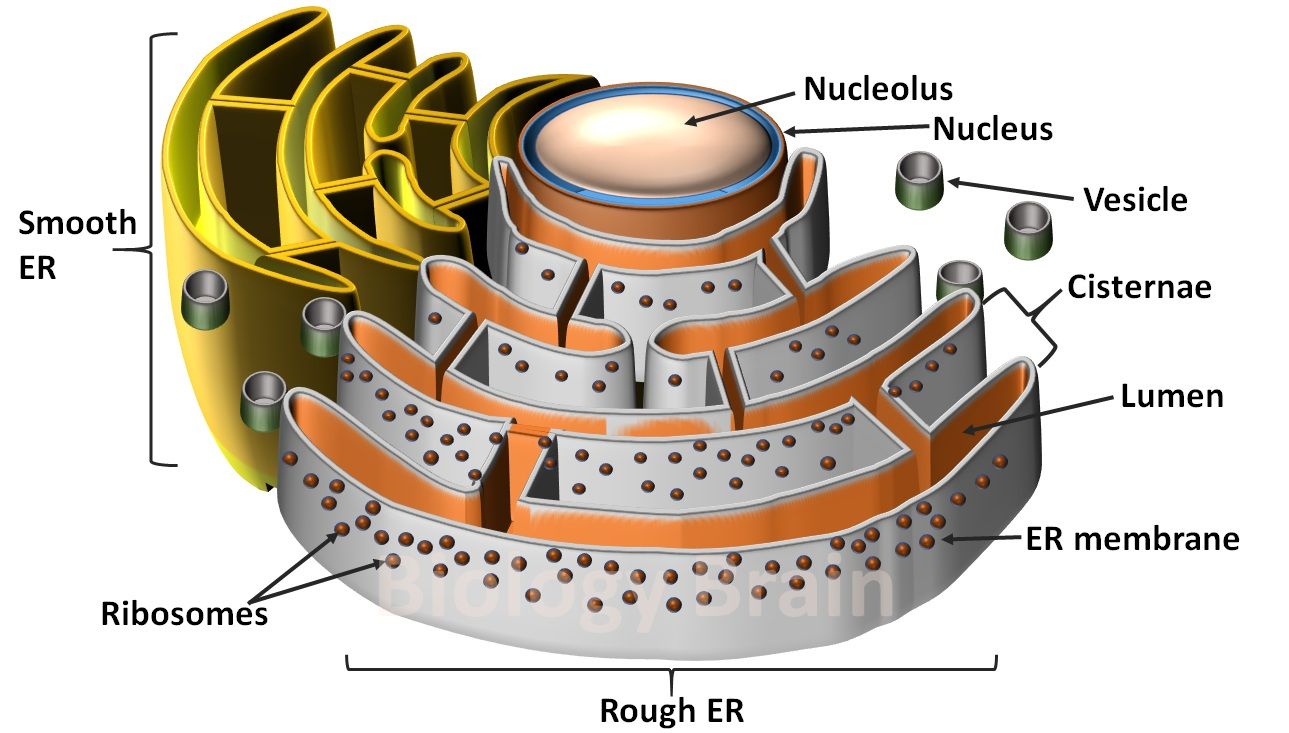
Diagram of Endoplasmic Reticulum Definition, Types, Function and Structure Biology Brain
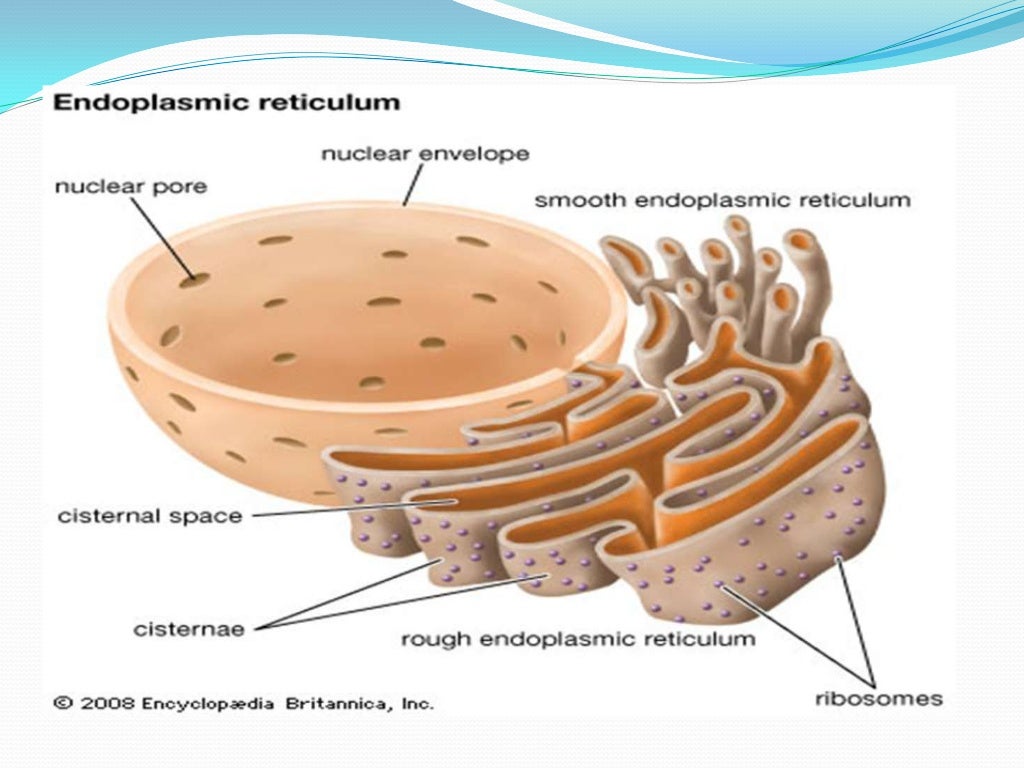
7 years ago. The Endoplasmic Reticulum in a eukaryotic cell is the transport network of the cell and it extends from and connects the nuclear membrane to the plasma membrane of a cell. But then whenever we draw a diagram of a typical plant or animal cell, we never extend it to the plasma membrane- we always leave it somewhere in the cytoplasm.
Endoplasmic reticulum the cellular inter definition, structure, function, and biology
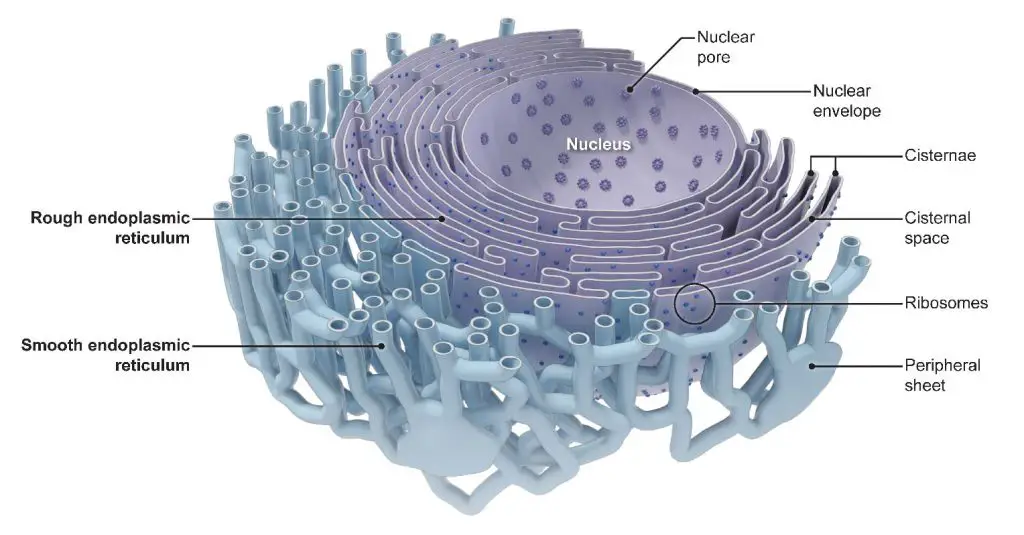
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a network of membrane-enclosed tubules and sacs (cisternae) that extends from the nuclear membrane throughout the cytoplasm (Figure 9.1). The entire endoplasmic reticulum is enclosed by a continuous membrane and is the largest organelle of most eukaryotic cells. Its membrane may account for about half of all cell membranes, and the space enclosed by the ER.

Endoplasmic reticulum is a continuous membrane, which is present in both plant cells, animal
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a large, dynamic structure that serves many roles in the cell including calcium storage, protein synthesis and lipid metabolism. The diverse functions of the ER are performed by distinct domains; consisting of tubules, sheets and the nuclear envelope. Several proteins that contribute to the overall architecture.
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER) — Structure & Function Expii
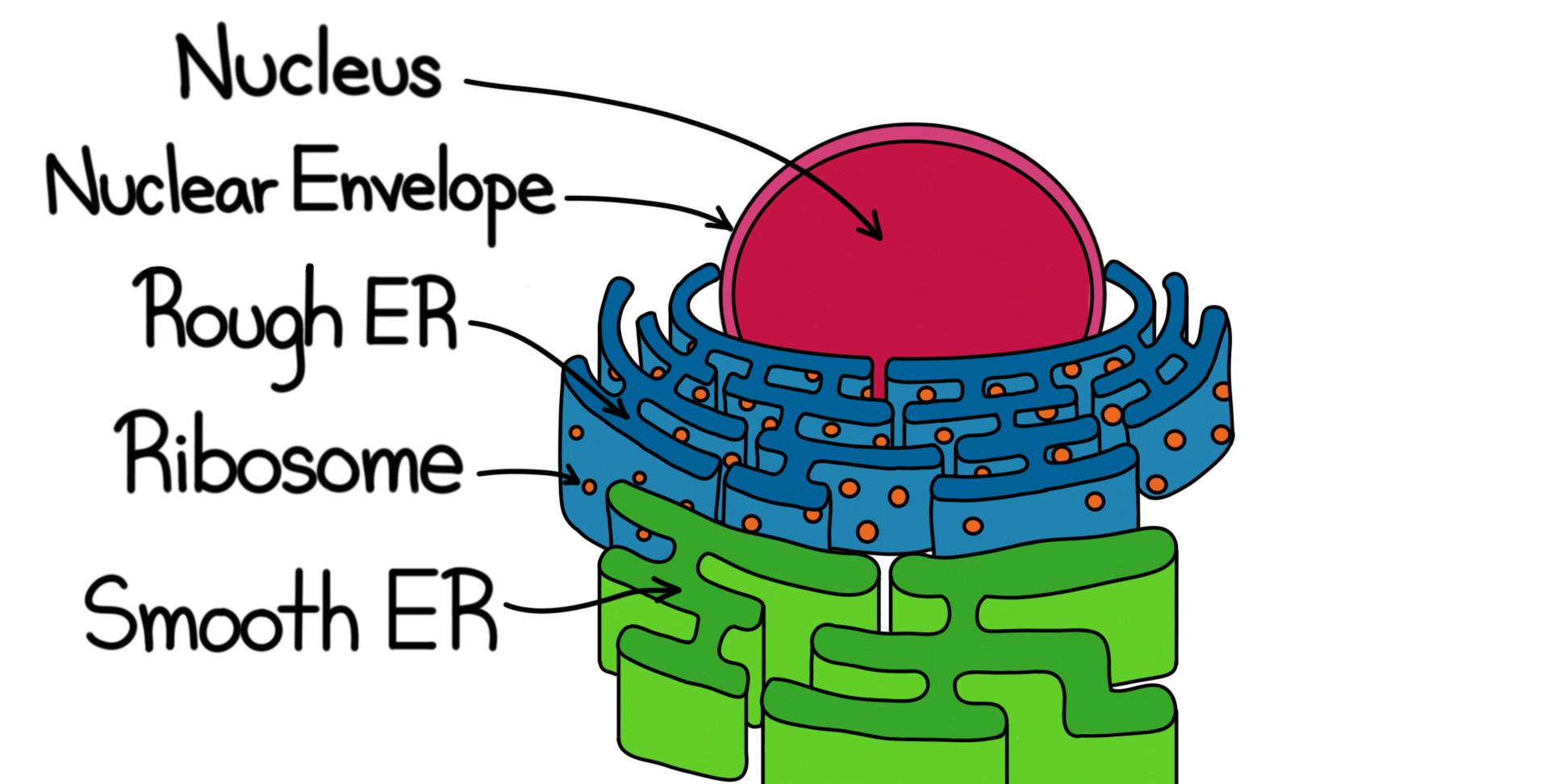
The endoplasmic reticulum is a network of tubules and flattened sacs that serve a variety of functions in plant and animal cells . The two regions of the ER differ in both structure and function. Rough ER has ribosomes attached to the cytoplasmic side of the membrane. Smooth ER lacks attached ribosomes.
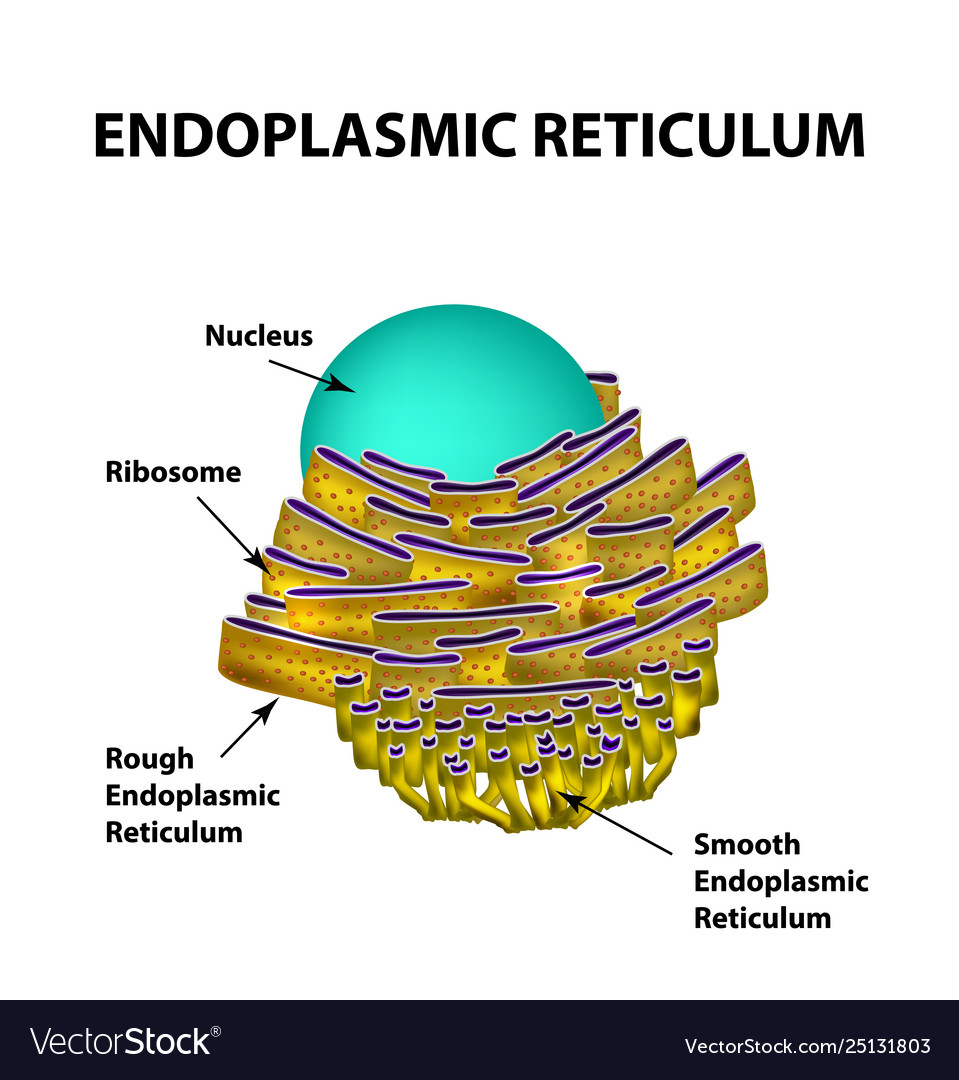
Endoplasmic reticulum structure infographics Vector Image
Endoplasmic reticulum can exist in two forms: rough ER and smooth ER. These two types of ER perform some very different functions and can be found in very different amounts depending on the type of cell. Rough ER (RER) is so-called because its membrane is dotted with embedded granules—organelles called ribosomes, giving the RER a bumpy.
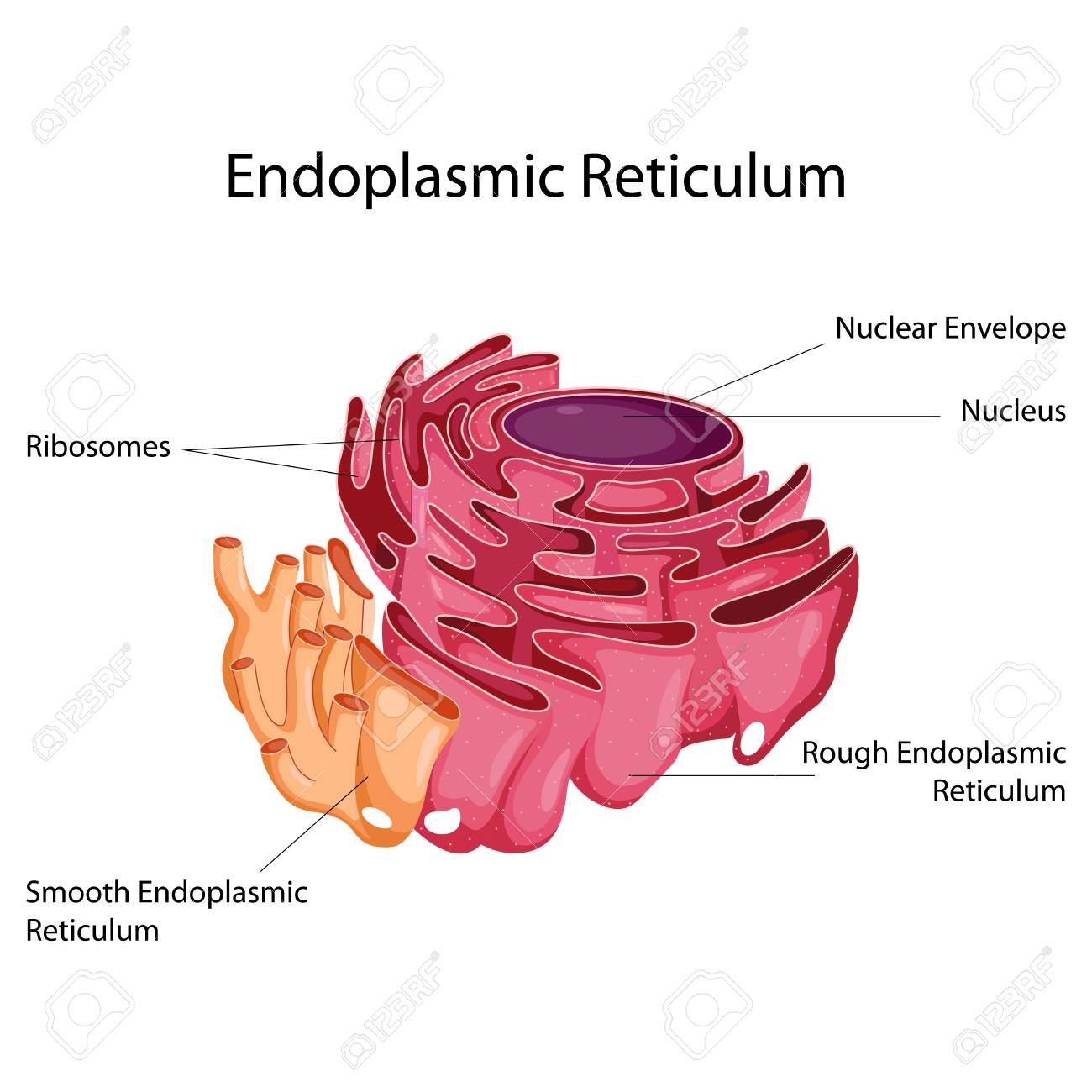
What Are Rough And Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum / Endoplasmic Reticulum Structure Types And
Micrograph of rough endoplasmic reticulum network around the nucleus (shown in the lower right-hand area of the picture). Dark small circles in the network are mitochondria.. The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is, in essence, the transportation system of the eukaryotic cell, and has many other important functions such as protein folding.It is a type of organelle made up of two subunits - rough.
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Structure, Functions and Diagram StudiousGuy
1.8: Endoplasmic reticulum. The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a complex system of membranes, tubules, cisternae and vesicles, appearing in two types: smooth and rough ER. Smooth ER is comprised of interconnected vesicles and cisternae that do not contain ribosomes. Smooth ER is involved in sterol biosynthesis, detoxification reactions and fatty.
Endoplasmic reticulum
3. List the functions of the endoplasmic reticulum. The endoplasmic reticulum performs the following functions: It is responsible for the production and secretion of steroid hormones. It is also responsible for the synthesis of essential lipids such as phospholipids and cholesterol. It is responsible for the metabolism of carbohydrates.
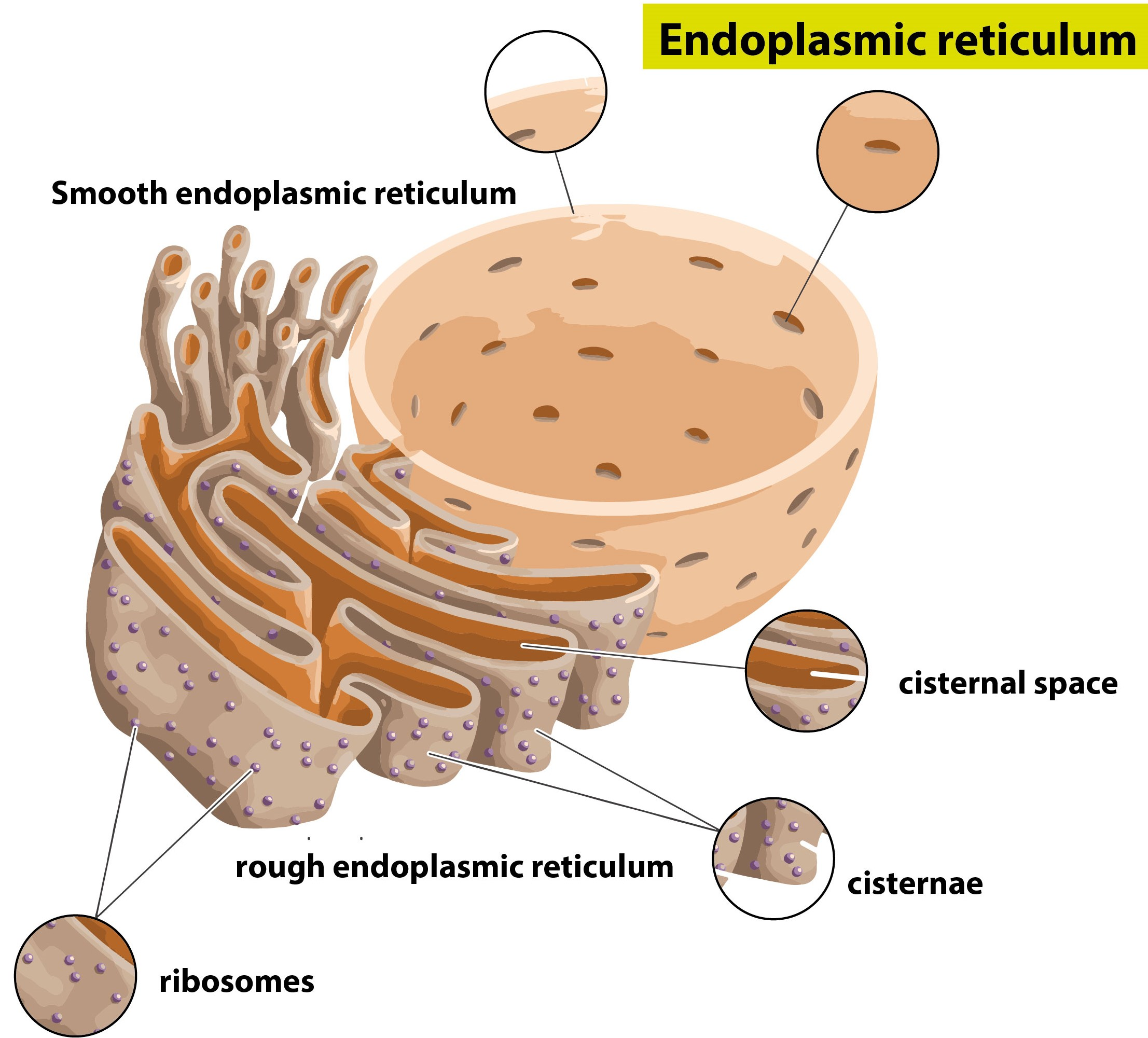
The surface of the endoplasmic reticulum is covered by (a) Glucose(b) DNA(c) Ribosomes(d) RNA
As I am sure you know, the ER (endoplasmic reticulum) is a network of cisternae around the nucleus. Thus, there is only one network of ER in a cell, but within that is a number of sacs and tubes that make up the entire ER. As for the Golgi apparatus (or body), is to is made up of multiple sections of cisternae (just like the ER, yet in a different formation), and there are often multiple.
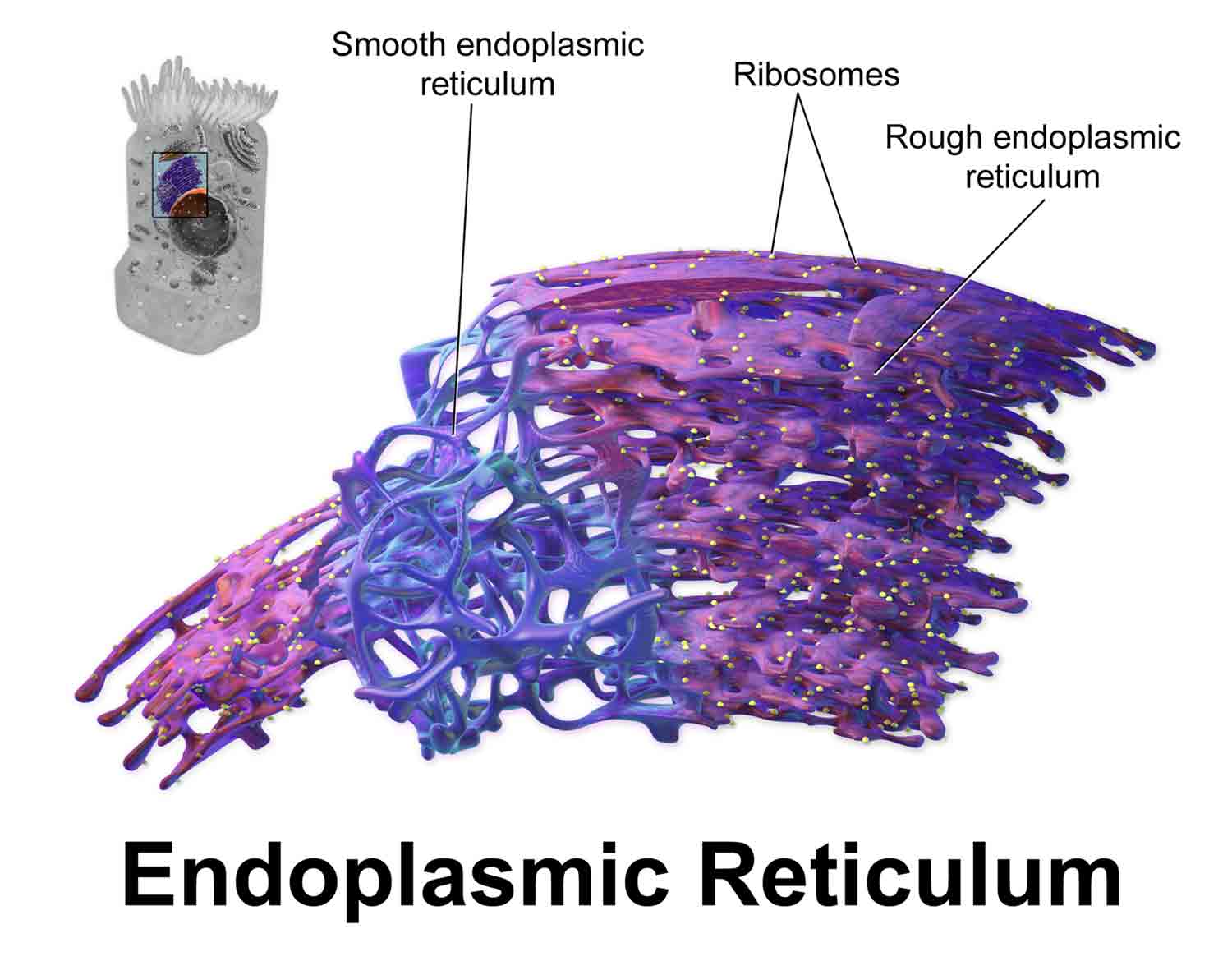
Kinds of Endoplasmic Reticulum Agranular and Granular Endoplasmic Reticulum
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a pivotal cell organelle, predominantly found in eukaryotic cells, and is integral to numerous cellular processes. It is the largest membrane-bound organelle, originating from the cell's nuclear envelope. The ER's primary roles encompass protein synthesis, modification, lipid synthesis, and the regulation.
/endoplasmic_reticulum-56cb365f3df78cfb379b574e.jpg)
The Structure and Function of the Endoplasmic Reticulum
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a series of interconnected membranous sacs and tubules that collectively modifies proteins and synthesizes lipids. However, these two functions are performed in separate areas of the ER: the rough ER and the smooth ER. The hollow portion of the ER tubules is called the lumen or cisternal space.